Wearables Defibrillators
- Dr ATHEENA MILAGI PANDIAN SHANMUGANATHAN
- Oct 31, 2024
- 2 min read
Wearable defibrillators represent a groundbreaking advancement in the field of emergency medicine and cardiac care, designed to provide life-saving interventions for individuals at risk of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). These innovative devices, often referred to as wearable cardioverter defibrillators (WCDs), are portable, lightweight, and equipped with advanced technology that allows for continuous monitoring of a patient's heart rhythm. By being worn directly on the body, typically in the form of a vest, wearable defibrillators offer a proactive approach to managing arrhythmias and can deliver electric shocks when needed to restore a normal heart rhythm. This capacity is particularly vital for patients who are not candidates for traditional implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) due to various medical reasons or for those who are waiting for surgical intervention.

The primary function of wearable defibrillators is to detect life-threatening arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation (VF) and ventricular tachycardia (VT), which are the leading causes of sudden cardiac arrest. These devices are equipped with sophisticated algorithms and sensors that continuously analyze the wearer’s heart rhythm. If a dangerous arrhythmia is detected, the device can deliver an appropriate shock to the heart, effectively restoring its normal rhythm and potentially saving the patient’s life. The automatic nature of this intervention is critical, as sudden cardiac arrest often occurs without warning, making it essential for timely treatment to be available at all times. In many cases, studies have shown that wearable defibrillators can significantly increase survival rates for patients experiencing life-threatening arrhythmias outside of a hospital setting, emphasizing their importance in acute cardiac care.

One of the most notable advantages of wearable defibrillators is their non-invasive nature. Unlike traditional ICDs, which require surgical implantation, WCDs can be donned and removed as needed, allowing for greater flexibility and comfort for patients. This feature makes wearable defibrillators particularly appealing for individuals recovering from cardiac events or procedures, as well as those with transient arrhythmias that may not require long-term monitoring. The user-friendly design of many devices also enhances patient compliance, as they can be easily worn under clothing and used in daily activities without significant disruption to the patient's lifestyle.
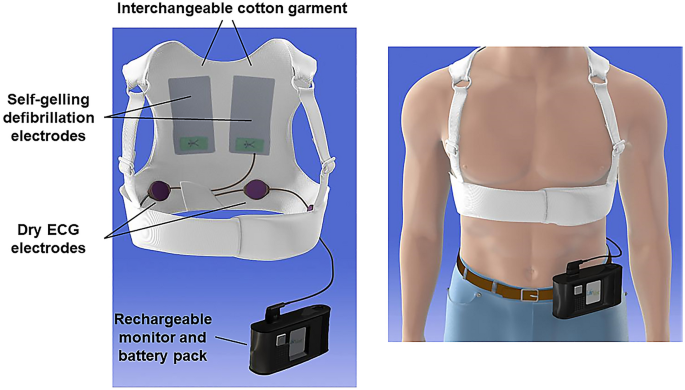
Wearable defibrillators have proven to be beneficial in various clinical scenarios. They are often prescribed for patients with recent myocardial infarctions (heart attacks), those with diagnosed cardiomyopathies, or individuals with a history of significant arrhythmias. Additionally, they serve as a bridge for patients awaiting heart transplants or those who are candidates for ICD implantation but cannot undergo the procedure immediately due to health complications.

By providing continuous cardiac monitoring during this critical period, wearable defibrillators offer peace of mind to both patients and healthcare providers, knowing that they have a reliable safety net in place to respond to life-threatening cardiac events.

Comments